This document outlines the steps for Kore users to integrate Kore Voice Automation with Amazon Connect, leveraging Amazon’s external voice transfer capabilities. This setup enables voice transfers from Amazon Connect to a Voice Gateway and back, facilitating a seamless call experience through the Amazon Connect desktop.
Architecture Diagram
Prerequisites
- AWS Console Admin access
- External voice transfer connectors per account with AWS Connect Instance enabled.
- A Kore voice AI Agent trained with few use cases.
Setup Instructions
1. Enabling External Voice Transfer in Amazon Connect
Before setting up the integration, you must enable the “External voice systems” option in your Amazon Connect instance. Refer to Set up Amazon Connect external voice transfer to an on-premise voice system for more information.
- Service Quota Increase: Submit a Service Quota Increase request to Amazon Connect. This feature is enabled only after Amazon Connect approves your request.
- Accessing the Option: Once approved, the “External voice systems” option becomes visible in your Amazon Connect console.

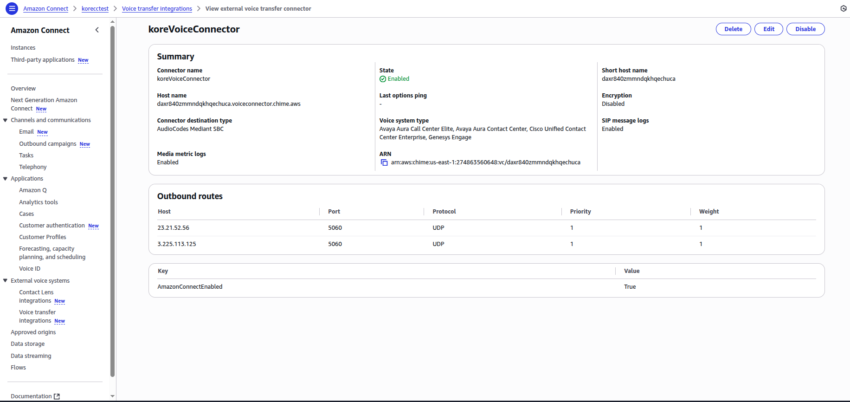
2. Creating an External Voice Transfer Connector
After enabling the feature, create a connector under Voice transfer integrations to link Amazon Connect with your Voice Gateway.
- Navigate to Connector Creation: Click the External voice systems option to access the connector creation screen.

- Connector Configuration:
- Name: Provide any desired name for the connector.
- Connector destination type: Select audio code from the dropdown list.
- Voice system type: Select one or multiple options; it does not affect the functionality.
- Encryption: Select Disabled.
- Logging: Select the option(s) to view the corresponding log in CloudWatch Logs for Connectors. It is recommended to select both the options.
- Host and Port Details: After creation, the connector configuration displays the IP address of the host, the protocol, and the port. This port should correspond to your external Voice Gateway environment.
For US Prod region of Kore:- IP address:
- 35.174.41.205
- 3.224.189.218
- Port: 5060
- IP address:
3. Configuring the Amazon Connect Flow
The next step involves modifying your Amazon Connect flow to utilize the newly created external voice connector.
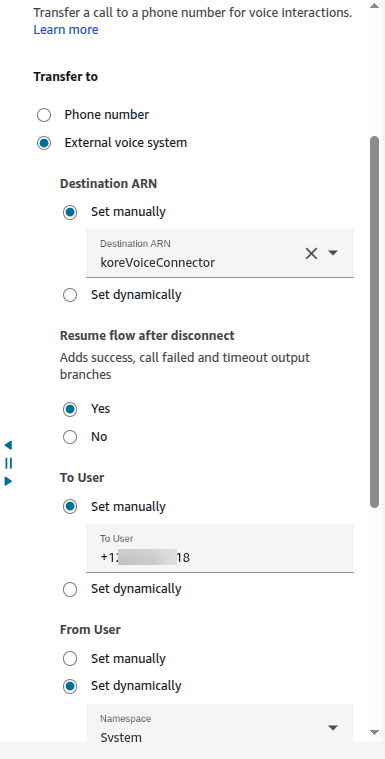
- Add “Transfer to Phone Number” Node: Within your Amazon Connect flow, add a “Transfer to phone number” node.
- Select External Voice System: Instead of entering a phone number, select the External voice system option.
- Attach Connector: Attach the specific connector you created in the previous step.
- Enable “Resume flow after disconnect”: Set this option to “Yes.” This step ensures that after the call ends with the third-party system (Voice Gateway), the call is transferred back to Amazon Connect, facilitating a continuous flow and correlation between Amazon Connect and the Kore system.
- To User: Enter a dummy phone number. You will configure this number as a DID number in SmartAssist > Voice > SIP Trunk Configuration, in later steps.
4. Configuring Contact Center AI (Kore Side Configuration)
On Kore side, specific configurations are required in Contact Center AI (CCAI) to receive and manage calls transferred from Amazon Connect.
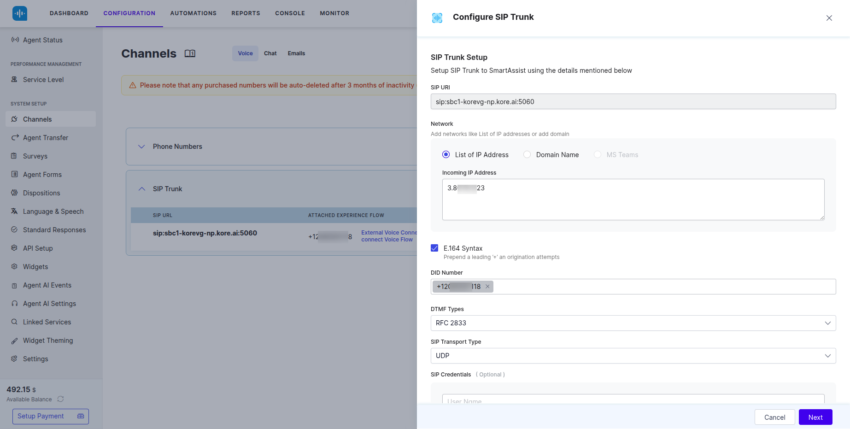
- Create New Configuration: In CCAI, create a new SIP Trunk (or use an existing one).
- Whitelist IP Address: The most critical step here is to whitelist the IP address provided by Amazon Connect. This IP address is essential for allowing communication from Amazon Connect to Kore. Check with Amazon Connect documentation or Support for the details on this IP address.
- DID Number: Provide the same Direct Inward Dialing (DID) number that will be used for the transfer (which was entered in the Transfer to phone number node in the previous step).
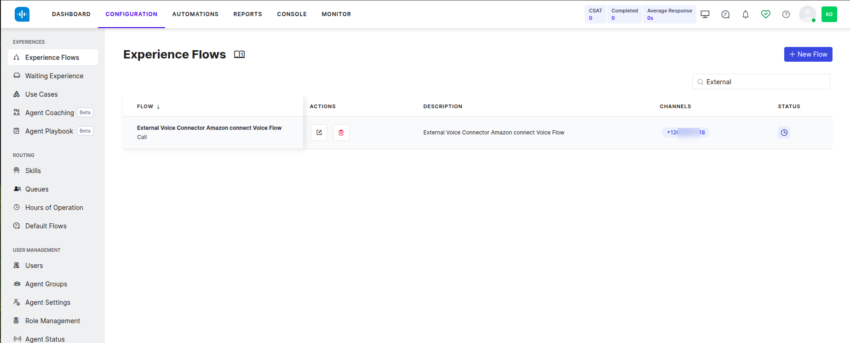
- Attach to Experience Flow: Once the configuration is complete, attach this number to the relevant Experience Flow within Kore.
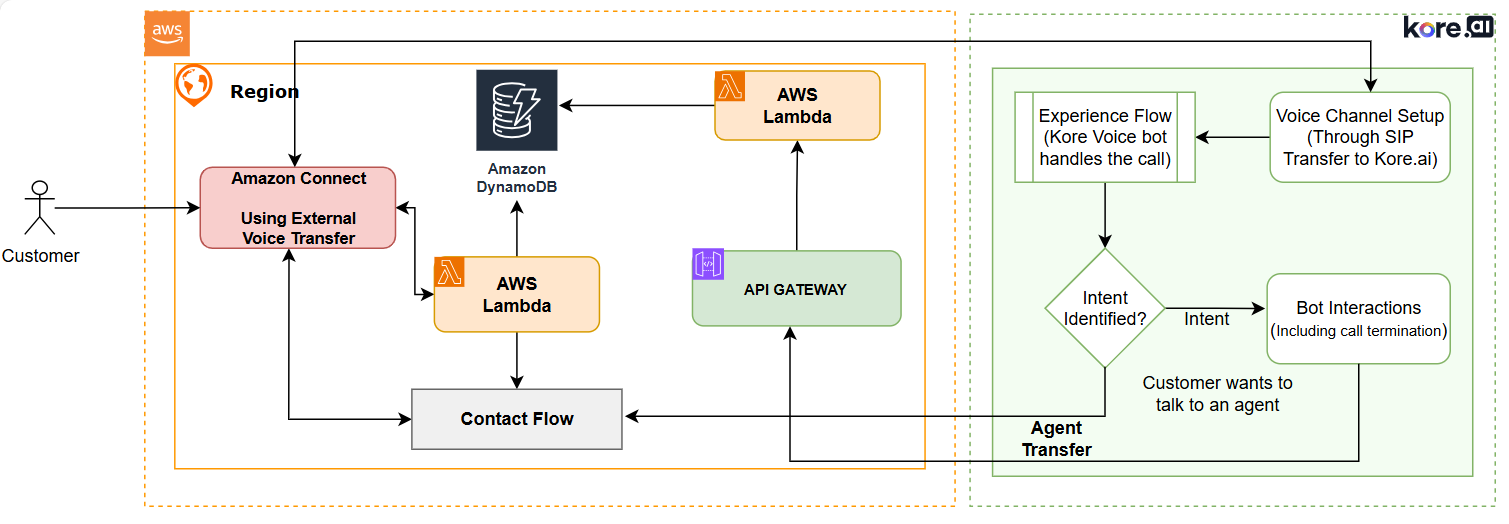
End-to-End Call Flow
The following steps describe the call flow after this integration:
- A call originates in Amazon Connect by calling the Amazon Connect number.


- The Amazon Connect flow transfers the call to Voice Gateway via the external voice connector.
- Kore CCAI handles the call. You can view the details of the call in the CCAI Dashboard > Interactions section.

- After interaction with Kore, the call is transferred back to Amazon Connect.

This setup provides a robust solution for leveraging Kore’s voice automation capabilities within your Amazon Connect Contact Center environment.
Metadata Passing from Kore to Amazon Connect (Additional Feature)
Currently, Amazon Connect does not support SIP header extraction. To pass metadata from Kore to Amazon Connect, use the following alternative AWS components:
- API Gateway
- Lambda function
- DynamoDB Table
- CloudWatch (for debugging)
Architecture
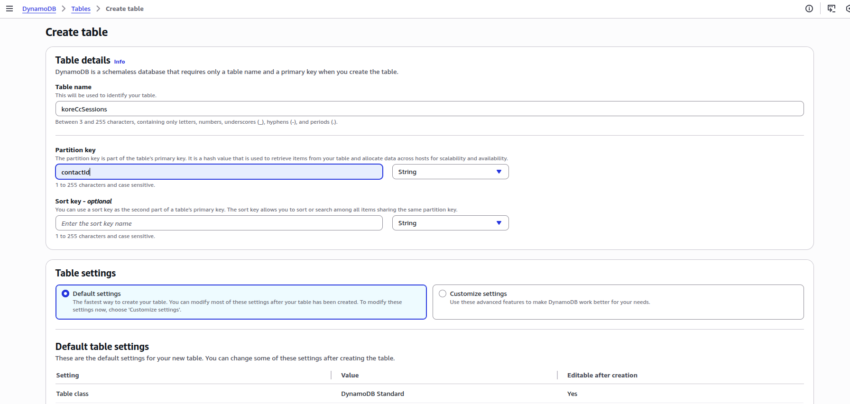
- Create a DynamoDB table with contactId (Amazon Connect Contact Id) as a partition key.
- Create an API Gateway and invoke from outside AWS (via the Kore Dialogtask > service Node, before agent transfer) to store data in the DynamoDB table.
- To call this API, the Amazon Connect contact ID must be passed as one of the query parameters. This ID is retrieved from the SIP headers data sent from Amazon Connect to Kore.
- Write two lambda functions—One for the API Gateway business logic and the other for its authentication.
- In the Amazon Connect flow, invoke another lambda function to extract these metadata saved in DynamoDB in the last step.
- These metadata values are then set as contact attributes within the flow.
AWS Side Configuration
Create a DynamoDB Table
Create Three Lambda Functions
You must create three lambda functions for three different purposes. All these lambda function runtimes should be in:
Runtime: python.
The recommended lambda function name and the internal code is given in the following section.
Once you paste the lambda code, deploy the latest version of the code. Ensure your first and third lambda functions have DynamoDB full access. (You can add permissions inside the IAM role of the lambda function.)
- koreStoreSessionMetadata: This lambda function is used to expose an API Gateway (Trigger) to get the metadata from Kore Platform and store it in the DynamoDB table. Copy and deploy the code from this link.
- AuthenticateBeforeStoringInDynamoDB: This lambda function is used to add an authentication layer (Authoriser) on the API Gateway mentioned in the previous lambda function (koreStoreSessionMetadata). Copy and deploy the code from this link.
- koreRetrieveSessionMetadata: This lambda is invoked in the Amazon Connect Contact Flow after the call gets disconnected from Kore and is handed over to Amazon Connect. This lambda returns all the metadata stored in the DynamoDB table using the first lambda. Copy and deploy the code from this link.
Create an API Gateway
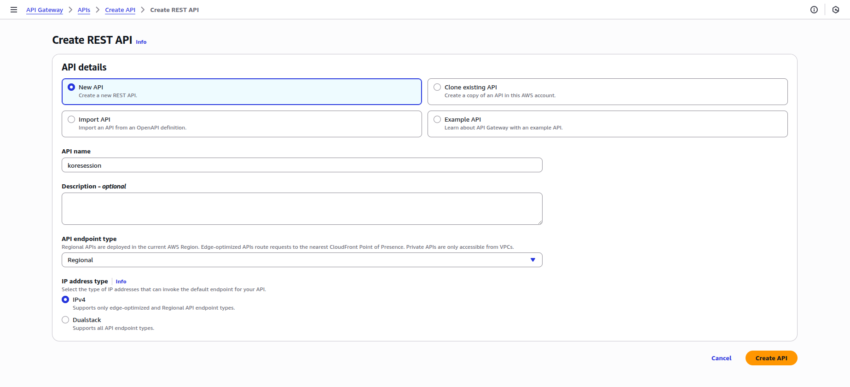
- Create a REST API Gateway with the default configuration:
- Create an API resource with the Resource path as “/kore-metadata.” Click Create resource:
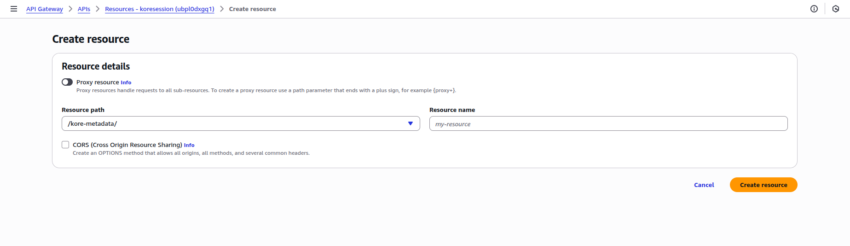
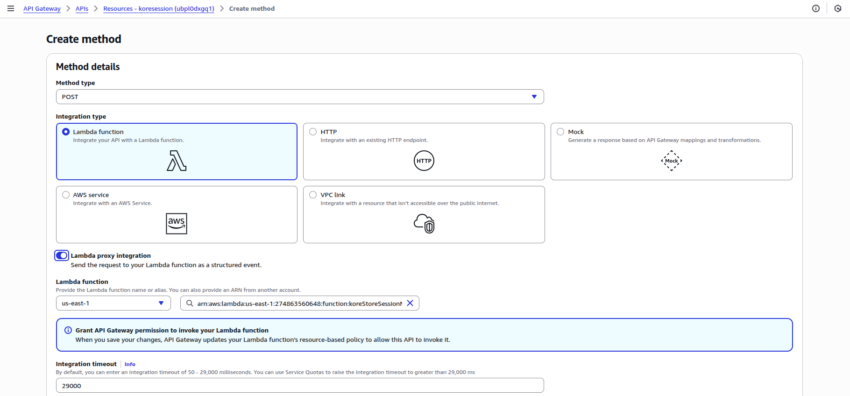
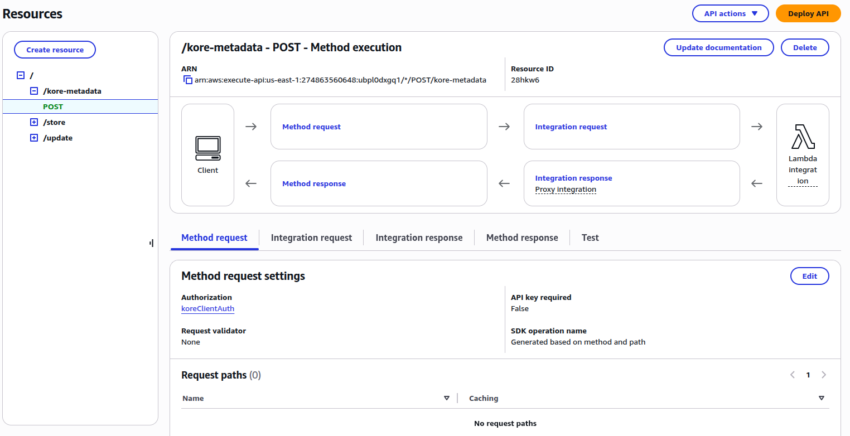
- Create an API Method with the following details:
- The created method appears as shown in the following screenshot:
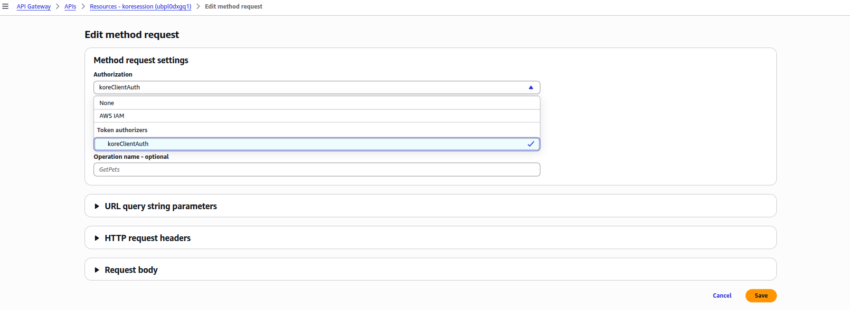
- To enable authentication for this API Gateway, you need Authorizers. Create a new Authorizer with the following details:
- Authorizer name: koreClientAuth
- Authorizer type: Lambda
- Lambda function: AuthenticateBeforeStoringInDynamoDB
- Lambda Event Payload: Select Token
- Token source: authorizationToken
- Token validation – optional: Enter the value you want to use as Token for the API authentication. You need the same value to store in the Env Variable of AuthenticateBeforeStoringInDynamoDB Lambda function with the key as AUTH_TOKEN.
- Click Create authorizer.
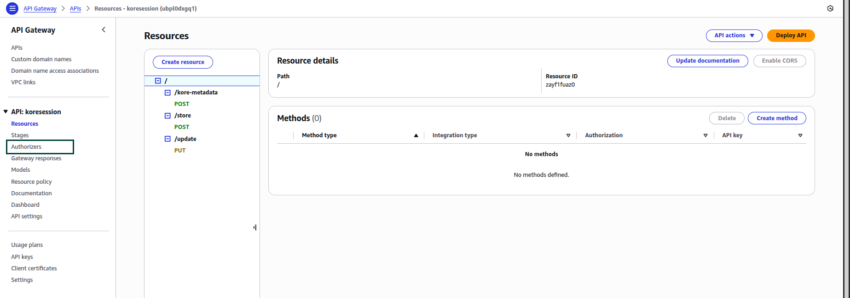
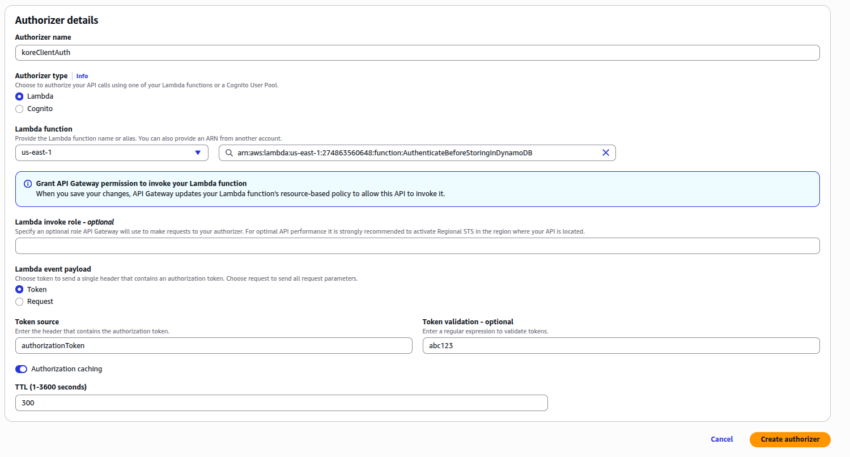
- Once the koreClientAuth Authorizer is created, add this as part of authentication for the API Resource and method you created.
- Click Deploy API.
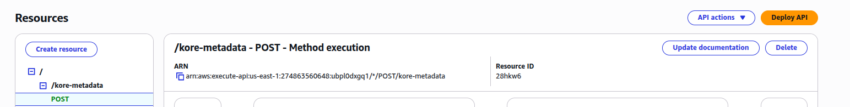
Modify the Contact Flow
Open the Amazon Connect instance and add the last lambda function (koreRetrieveSessionMetadata) inside the flow.
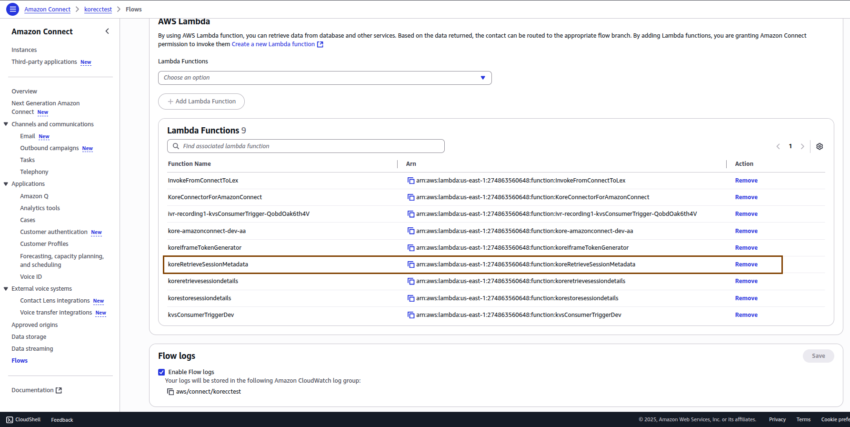
Modify the Amazon Connect flow:
- Name this flow as TransfertoKore&MetadataPassing. (You will reference this name later during the Agent AI integration step.)
- Add an AWS Lambda function node after the Transfer to phone number node.
- In the AWS Lambda function:
- Select the Invoke Lambda function (koreRetrieveSessionMetadata), which was added in the last step.
- Add a parameter:
- Destination Key: contactId (enter this name)
- Value: set dynamically
- Namespace: System
- Key: Contact id
- Response Validation: JSON
- Save the configuration.
- Add one Set contact attribute node. In this node:
- Set attributes on: Current Contact
- Add another attribute
- Namespace: User defined
- Key: customData
- Value to be Set dynamically
- Namespace: External
- Key: body
- Save the configuration.
- Connect all the nodes, and you can add a Play prompt node to understand if there is any error in the flow.
- Save and Publish the flow.
- The modified Amazon Connect flow appears as shown in the following screenshot:
Kore Side Configuration
In SmartAssist
- Experience Flows
- Open the Experience Flow.
- Add the following code snippet in a Script node immediately after the Start node:
setCallFlowVariable('sipHeaders', context.BotUserSession.channels[0].handle.sipHeaders); var headers = getCallFlowVariable('sipHeaders'); userSessionUtils.put('sipHeaders', headers); - Click Publish to publish the flow.
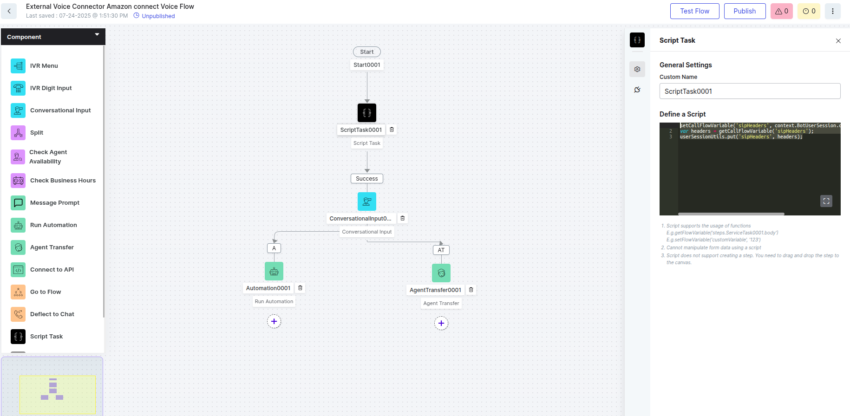
- Identify the Automation bot used in the Experience Flow. You will need it in the next step when configuring the Botbuilder.
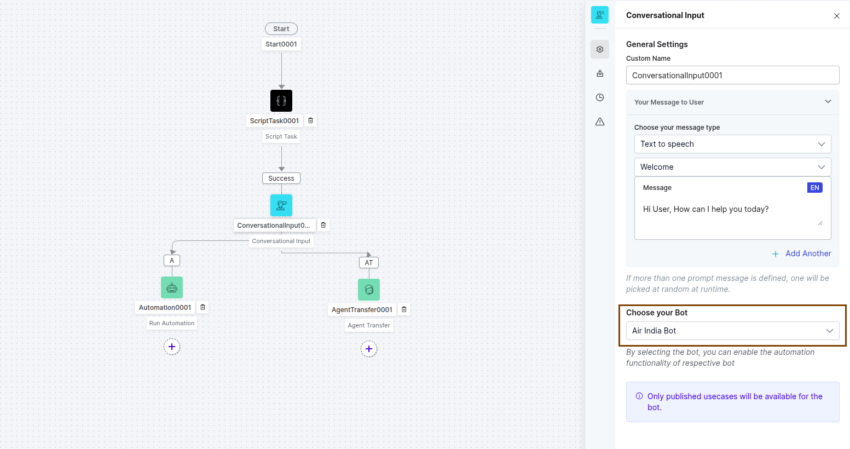
- Agent Transfer
- Go to SmartAssist > Configuration > System Setup > Agent Transfer.
- Click SIP Transfer.
- Select SIP BYE from the SIP Transfer Method list.
- Click Done to save the configuration.
In Botbuilder
Ensure the Automation bot used in the SmartAssist Experience Flow includes an Agent Transfer dialog task.
- Open the Agent Transfer Dialog Task.
- Add a Script node and paste the following code to extract contactId (Amazon Connect contact Id) from the SIP headers:
try{ var headers = context.session.UserSession.sipHeaders; if(headers){ var contactId = headers.find(o => o.name === 'X-Amzn-ConnectContactId'); if(contactId){ BotUserSession.put("ContactId", contactId.value); } } }catch(err){ koreDebugger.log("Error is:"+err); } - Add a Service node immediately after the Script node to make a REST API request to the API Gateway configured inside AWS in the earlier steps.
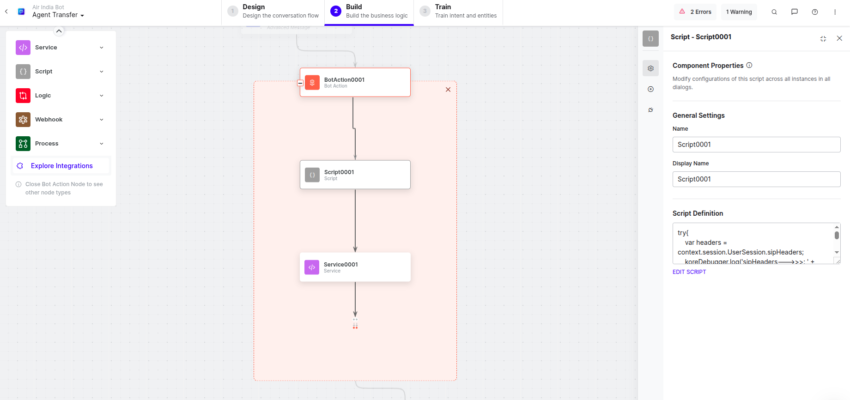
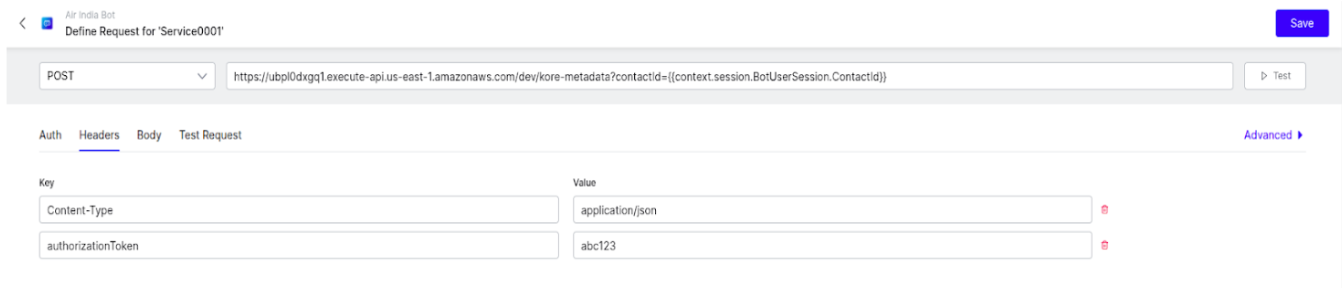
- Click Define Request in the Service node.
Add the Request URL: Add the API Gateway URL with contactId as query parameter. Get this by accessing your first lambda function (“koreStoreSessionMetadata”) > Configuration >Trigger.
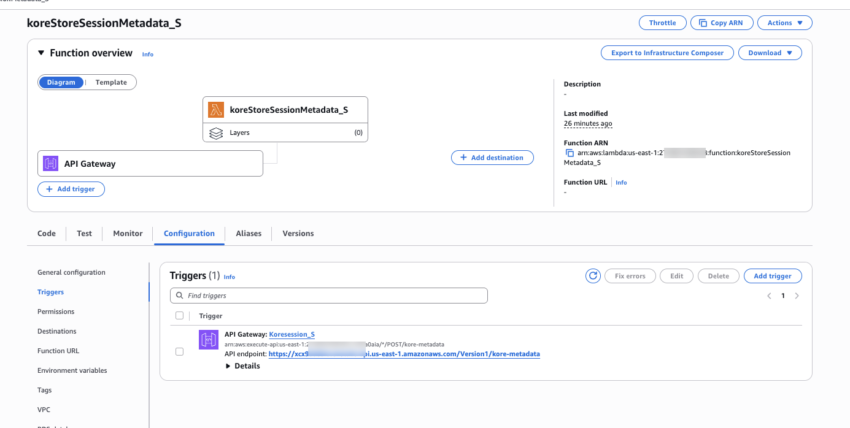 Example: https://ubpl0dxgq1.execute-api.us-east-1.amazonaws.com/dev/kore-metadata?contactId={{context.session.BotUserSession.ContactId}}
Example: https://ubpl0dxgq1.execute-api.us-east-1.amazonaws.com/dev/kore-metadata?contactId={{context.session.BotUserSession.ContactId}}
-
- Body:
- Add your metadata
Example:
{"x_metadata":"Hello from Kore", "kore-instanceSessionId":"{{context.session.BotUserSession.lastMessage.messagePayload.instanceSessionId}}"}Note: Pass the kore-instanceSessionId key and its value in the above specified format. This is required for the Agent AI widget to retrieve the user’s bot history. You may also include additional data, as needed.
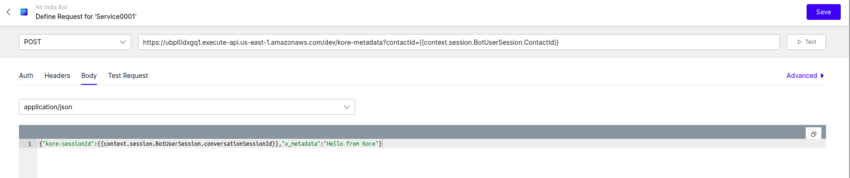
- Add your metadata
- Body:
- Save the configuration.
- Publish the bot.
-
Validate Your Metadata
When you call the Amazon Connect number, the call routes to Kore Automation and, after agent transfer, returns to the Amazon Connect desktop.
To view the metadata, check the Flow CloudWatch logs or use Contact Search:
- Sign in to Amazon Connect.
- Click Analytics and optimization > Contact search.
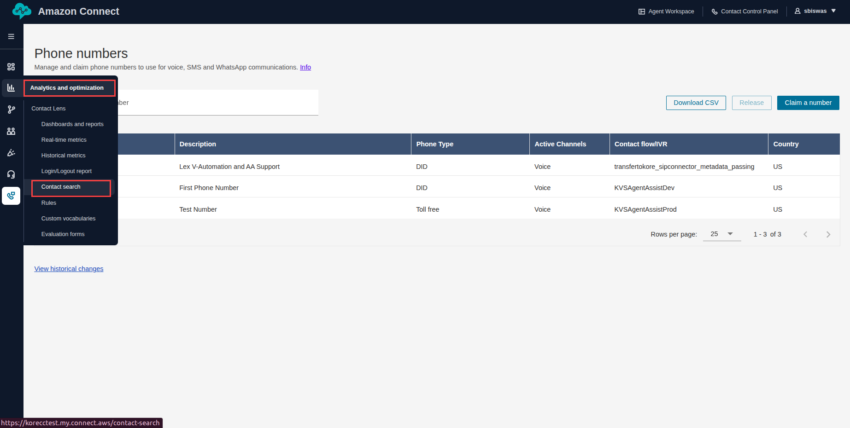
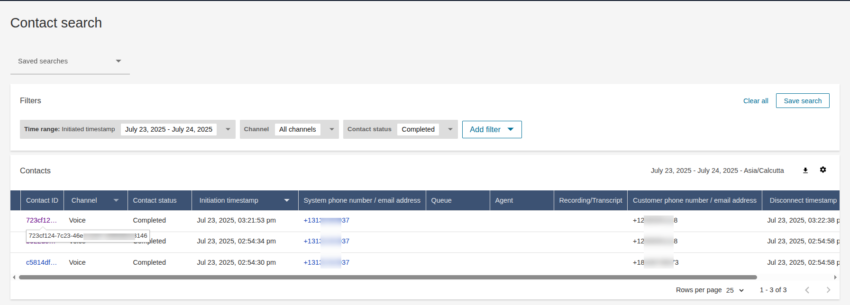
- A list of conversations is displayed. You can also filter the results by contact ID.
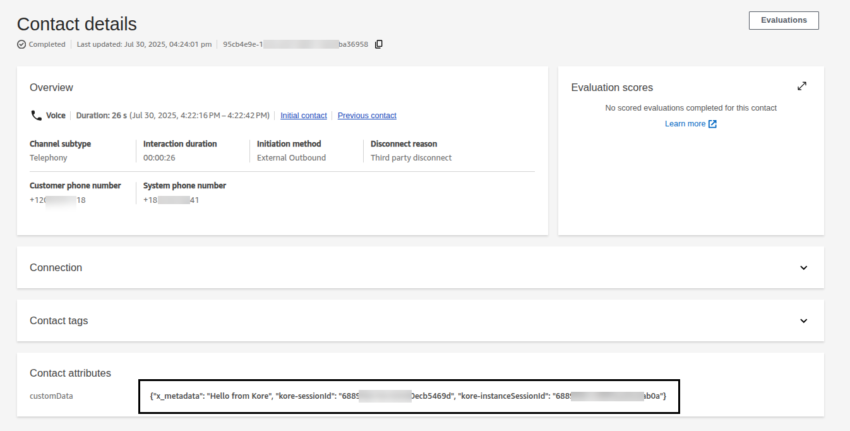
- When you open a contact’s details, the metadata appears as contact attributes.
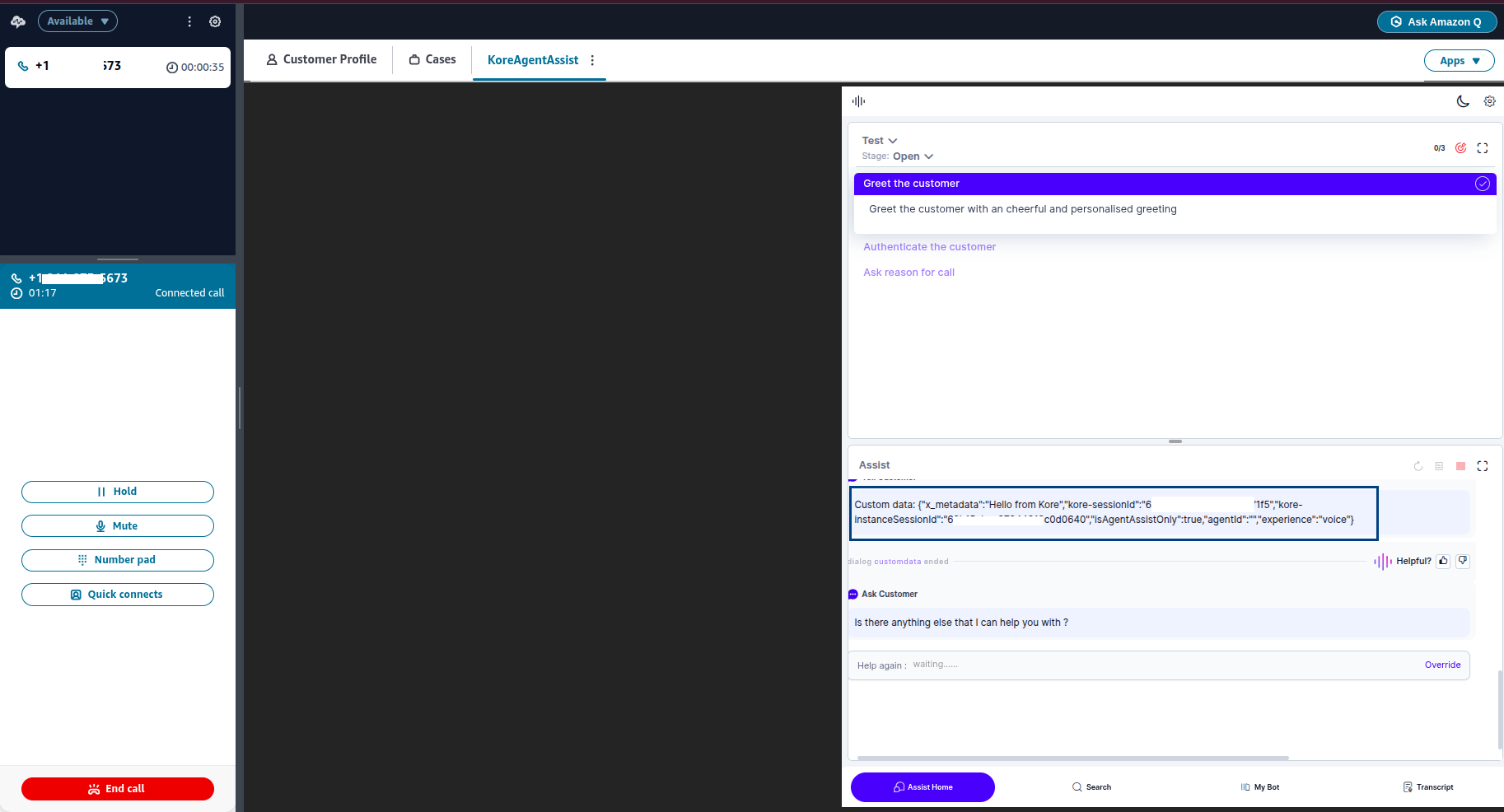
Passing Metadata as Custom Data to Agent AI
To integrate Agent AI as a third-party application (TPA) into the Amazon Connect workspace, follow this document.
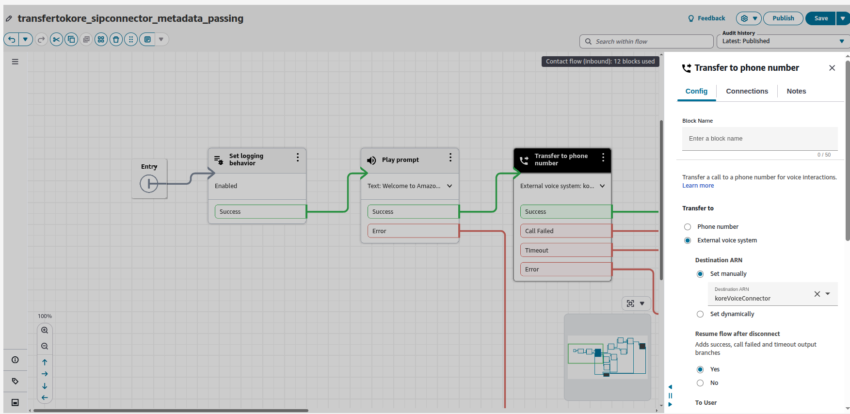
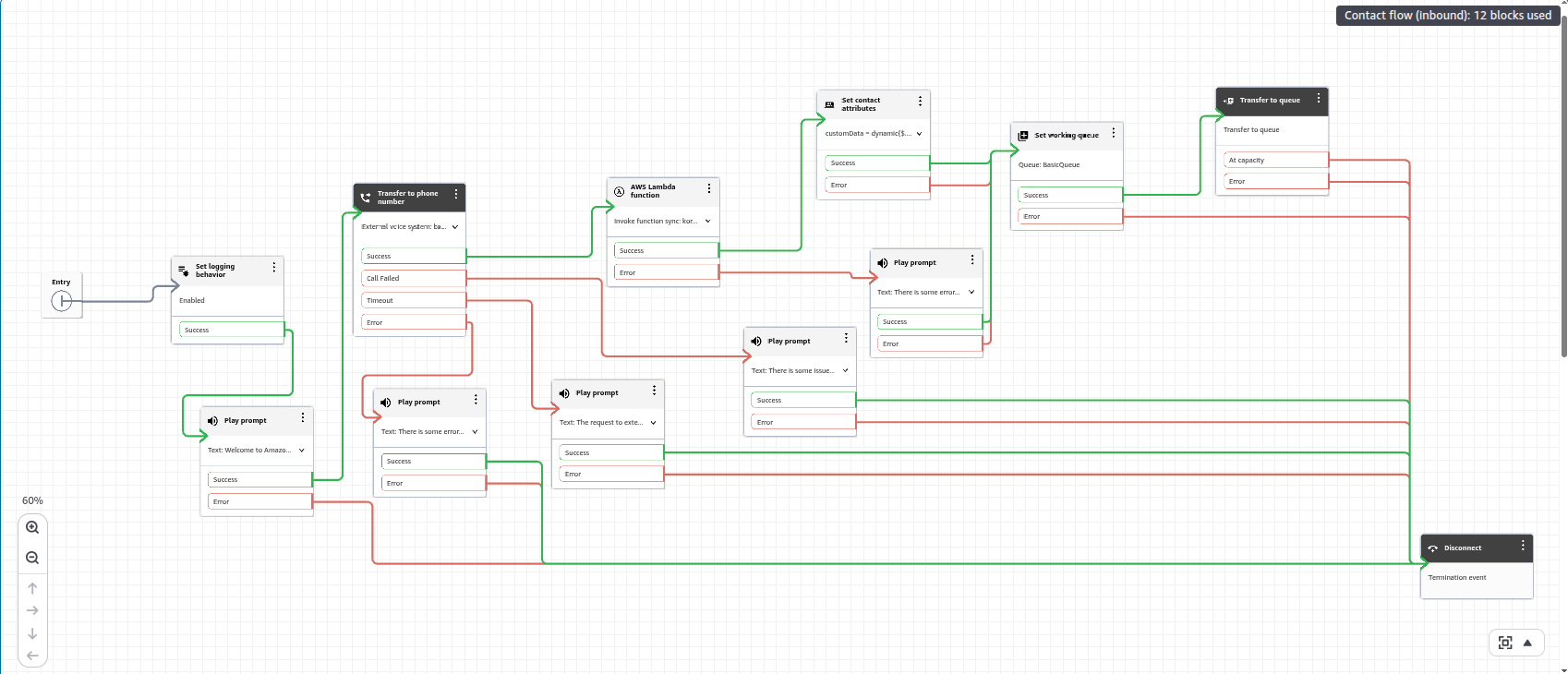
Modify the Amazon Connect flow
After integrating Agent AI as a TPA in Amazon Connect, you must have created another contact flow (for example, KVSAgentAssist). Add this flow to the previously created or imported flow (TransfertoKore&MetadataPassing).”
The final screenshot of the contact flow appears as shown below:
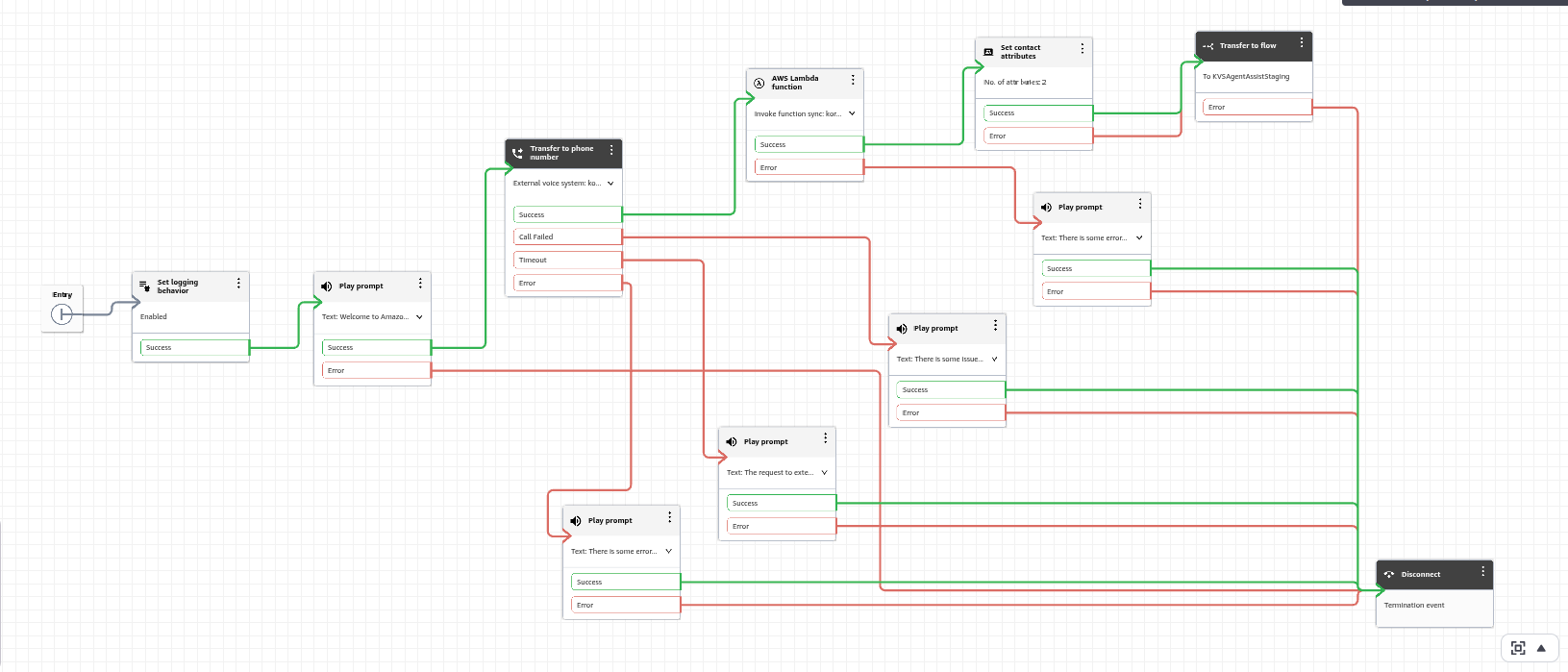
Any metadata passed from Kore to Amazon Connect in the previous steps becomes available in the Agent AI widget after it loads.
To pass metadata from the Amazon Connect contact attribute named customData, the data is collected at runtime and passed to the Agent AI widget during its creation.
You can access this custom data in the Agent AI widget under the following path:
context.session.UserContext.customData
After accepting the call and loading the Agent AI widget, you can print the custom data as shown below: