Business Rules allow you to define rules that personalize and fine-tune the search results based on various business requirements and user contexts.
Rules, for example, can also be used in merchandising scenarios to launch promotions and offers with quantity discounts or time-bound festive offers. Rules are based on user context, search context, page context, or a combination of contexts. Rules can define how results are promoted, positioned, or filtered.
For example, on an e-commerce site, based on the geographical location availability of certain products or their variants can be hidden, or if the user is logged in from a mobile device the number of search results displayed needs to be reduced due to limited screen space.
More About Business Rules
SearchAssist lets you define the cause and effect dimensions of Business Rules: conditions (cause) and outcomes (effect).
Conditions
Conditions define the trigger, based on the context and parameter values. Context can be:
- Search context Based on user search history, it has predefined attributes such as Recent Searches, Current Search, Traits, Entities, Keywords, Semantic meanings identified
- Page context Based on predefined attributes such as Device, Browser, Current page, Recent pages, and Location and other required attributes of a page, it can be passed from the website through the SDK.
- User Context Based on user information that a website can pass through SDK.
Parameters include setting the preceding context to contain/not contain/equals/not equals to a given keyword
Outcome
Define what happens when there is a condition match. The outcome can be an action and response. Action can be one of the following:
- Boost a particular response set to promote the results to display at the top.
- Lower a particular response set to demote the results from displaying at the top.
- Hide a particular response set to prevent certain results from showing to the search user.
- Filter a particular response set to screen certain search results by default.
Response enables a predefined field filter when a condition is met. The trigger that enables a response can be a static keyword, or a dynamic keyword taken from the context. For example, the end-user enters a query, “show me car insurance FAQs.” SearchAssist searches the index and only displays FAQs with relevant car insurance content.
Scenarios
The following scenarios demonstrate how a user could apply business rules.
Banking scenario
Present premium customers with a credit card offer. Define a rule as follows:
- CONDITION: “Search Context: RecentSearches” Contains “Credit” OR “Card”
AND “User Context: CustomerType” Contains “Premium” - OUTCOME: “Boost Results” Containing “Title: Card Offers” OR “Title: Card Rewards”
If the user is not creditworthy, you do not want to show them loan offers. Define a business rule as follows:
- CONDITION: “Search Context: RecentSearches” Contains “Loan” OR “Credit”
AND “User Context.CustomerInfo.CreditWorthy” Contains “Poor” - OUTCOME: “Hide Results” Containing “Loans: Loan” OR “Loans: Credit”
If the user has only a savings account and is searching for account-related information, you do not want to show information related to other types of accounts (e.g. checking accounts). Define a business rule as follows:
- CONDITION: “User Context.AccountType” Contains “Savings”
AND “User Context: AccountType” Doesn’t Contain “Checking”
AND “Page Context: PageName” Contains “Account” OR “Banking”
AND “Search Context: CurrentSearch” Contains “Information” OR “Details” - OUTCOME: “Filter Results” Containing “Title: Savings”
Applying Business Rules
Follow these steps:
- Click the Indices menu tab.
- In the left pane, click Business Rules.
- On the Business Rules page, click Add Rules.
- In the Add Rule dialog box, enter a unique name.
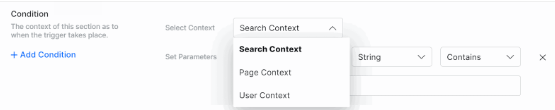
Adding Conditions
Under the Conditions section:
- Search Context Optimize results based on search context. For example, recent searches, current search, and traits.
- Page Context Assign data specifically to a page. For example, context-based on the current page, recent page, browser, or device.
- User Context Assign data specifically to a search user. For example, User Type (e.g. Premium User, Normal User, User Profile, Age).
- Click Select Context and select an option on the drop-down menu.
- Search Context Optimize results based on search context. For example, recent searches, current search, and traits.
- Page Context Assign data specifically to a page. For example, context-based on the current page, recent page, browser, or device.
- User Context Assign data specifically to a search user. For example, User Type (e.g. Premium User, Normal User, User Profile, Age).
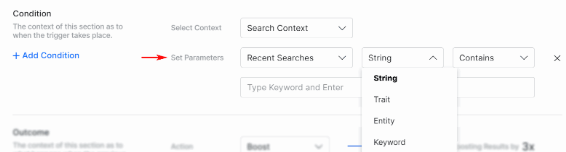
- Configure the parameters.
- Select the parameters available for the corresponding context from the Set Parameters dropdown lists.
- Set the Data Type expected for the parameter.
- Set the condition to Contains/Does not Contain/Equals to/Not Equals to.
- Set the keyword to be compared with, and add multiple keywords by hitting enter after each entry.
- To add more conditions, click +Add Condition.
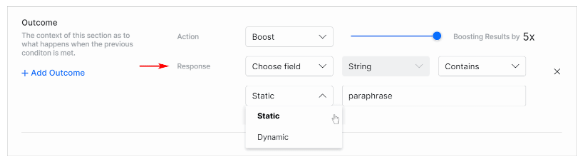
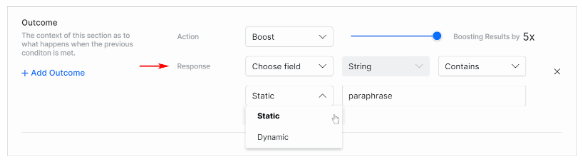
Setting Outcomes
In the Outcome, section:
- Click the Action field and select an option.
- Boost the results by x times (max 5x times).
- Lower the results by x times (max 5x times).
- Hide the results based on the preceding conditions.
- Filter the results based on the preceding conditions.
- Select the parameters from the Response drop-down list:
- Choose the field to be considered for the response.
- Review the Data Type field auto-populated by the SearchAssist.
- Set the condition to Contains/Does not Contain Equals to/Not Equals to.
- Choose Static or Dynamic keyword based on the context values.
- Set the keyword to be compared with; add multiple keywords by hitting enter after each entry.
- To add more outcomes, click +Add Outcome.
- Click Add.
Once added, you can perform the following actions on the rules: