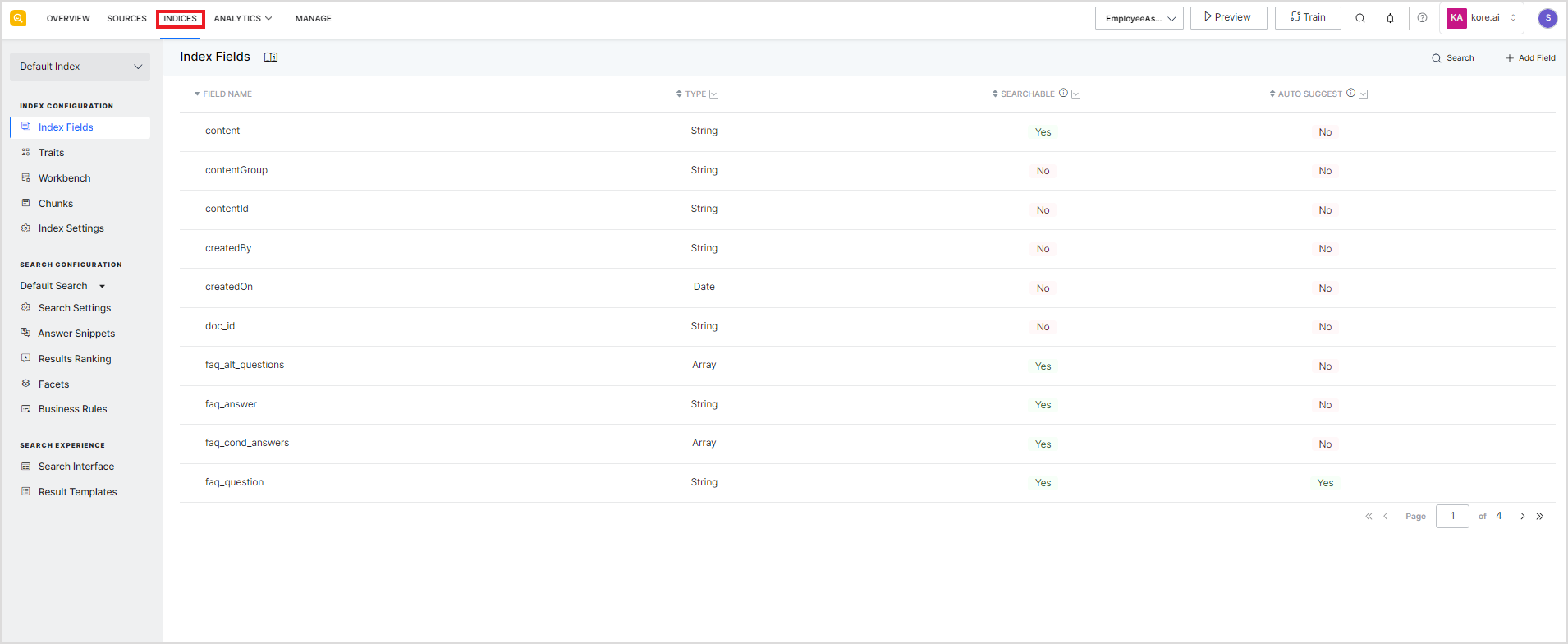
Indexing is the technique by which search engines organize the data ingested from the content sources to enable efficient and rapid retrieval of relevant information in response to user queries. The indexing process includes the identification of the indices from the content, pre-processing, and structuring of the data in an index. An index is like a data structure which stores data of a particular kind. The indexing process contributes to the overall effectiveness of the search.
Index Configuration refers to the set of parameters and rules used for preparing the index for the data. For a SearchAssist application, an Index Configuration consists of:
- Configuration parameters to identify Index Fields and process them in stages to prepare search results index or answers index.
- Search Settings are used to fine-tune the relevance of the fields as per the requirements.
- Search Experience parameters that define the result templates.
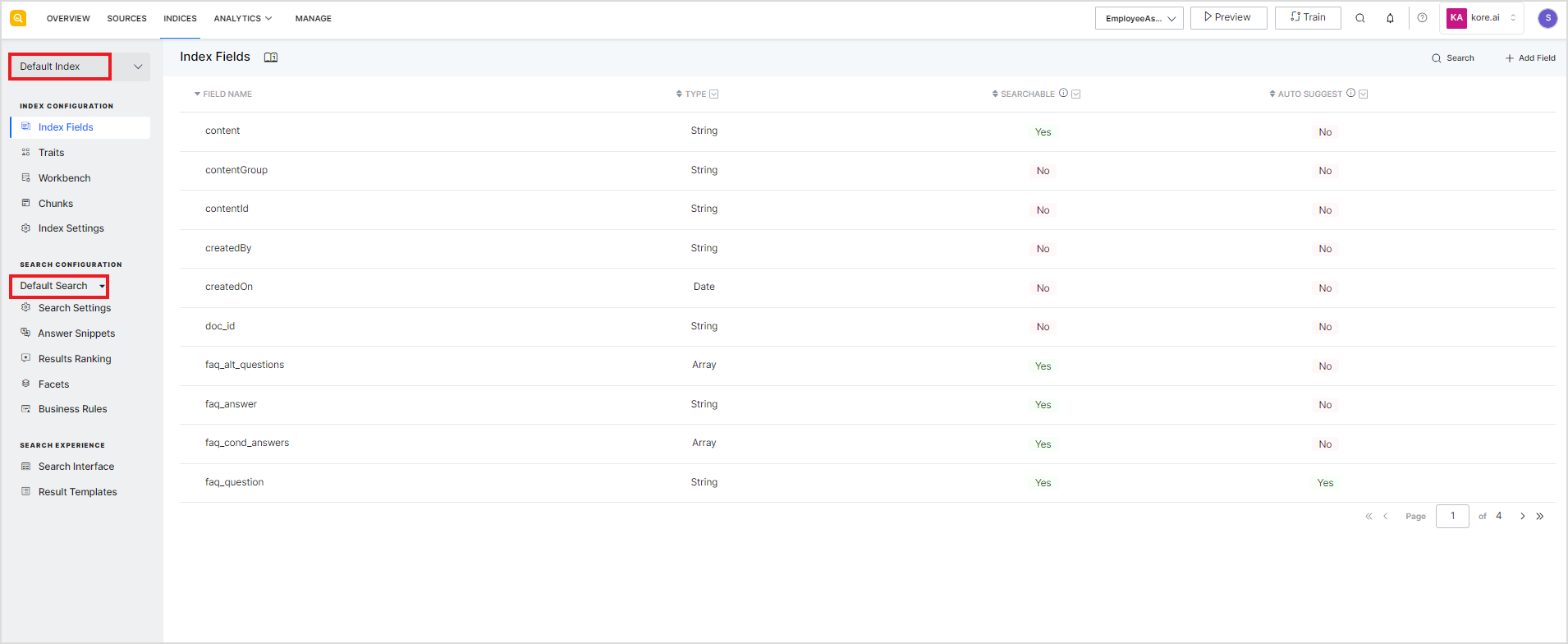
Go to the Indices section in SearchAssist to manage the Index Configurations.
By default, every SearchAssist application comes with a Default Index Configuration and a Default Search Configuration.
You can choose to edit the existing configurations or create new Index and Search configurations.
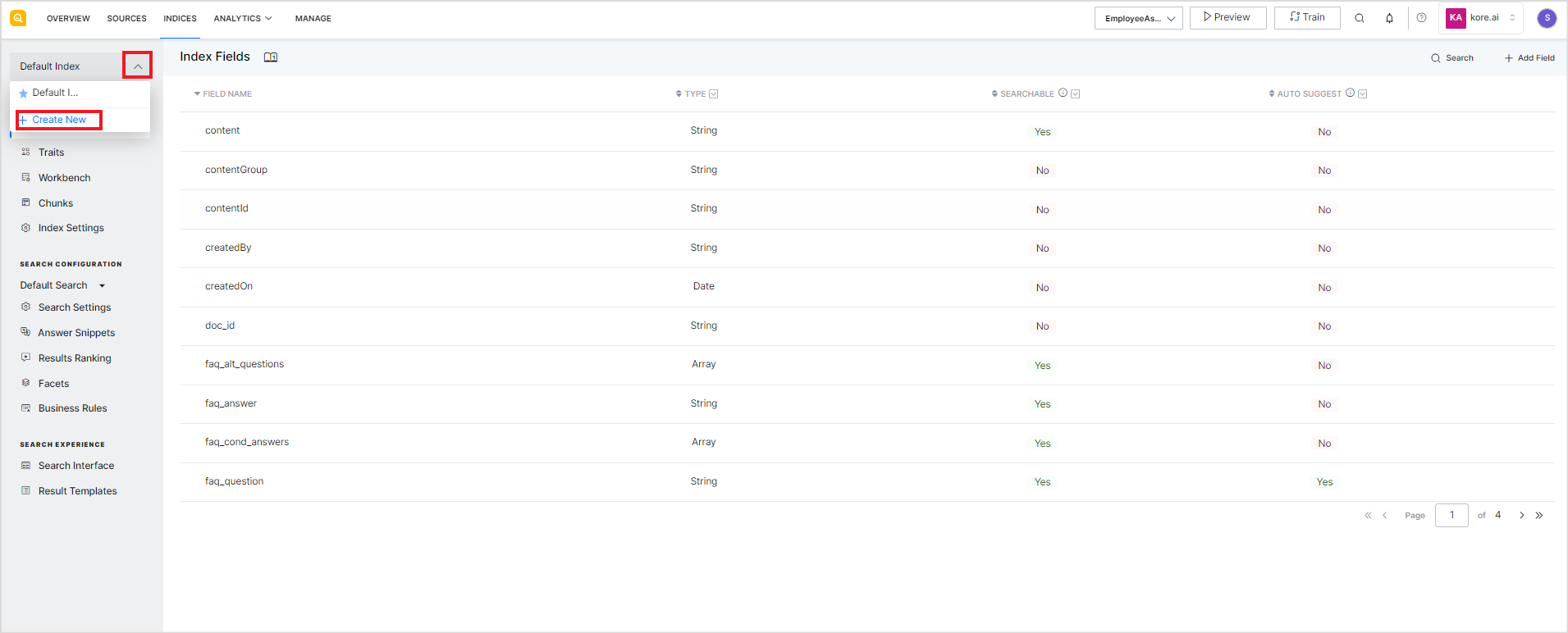
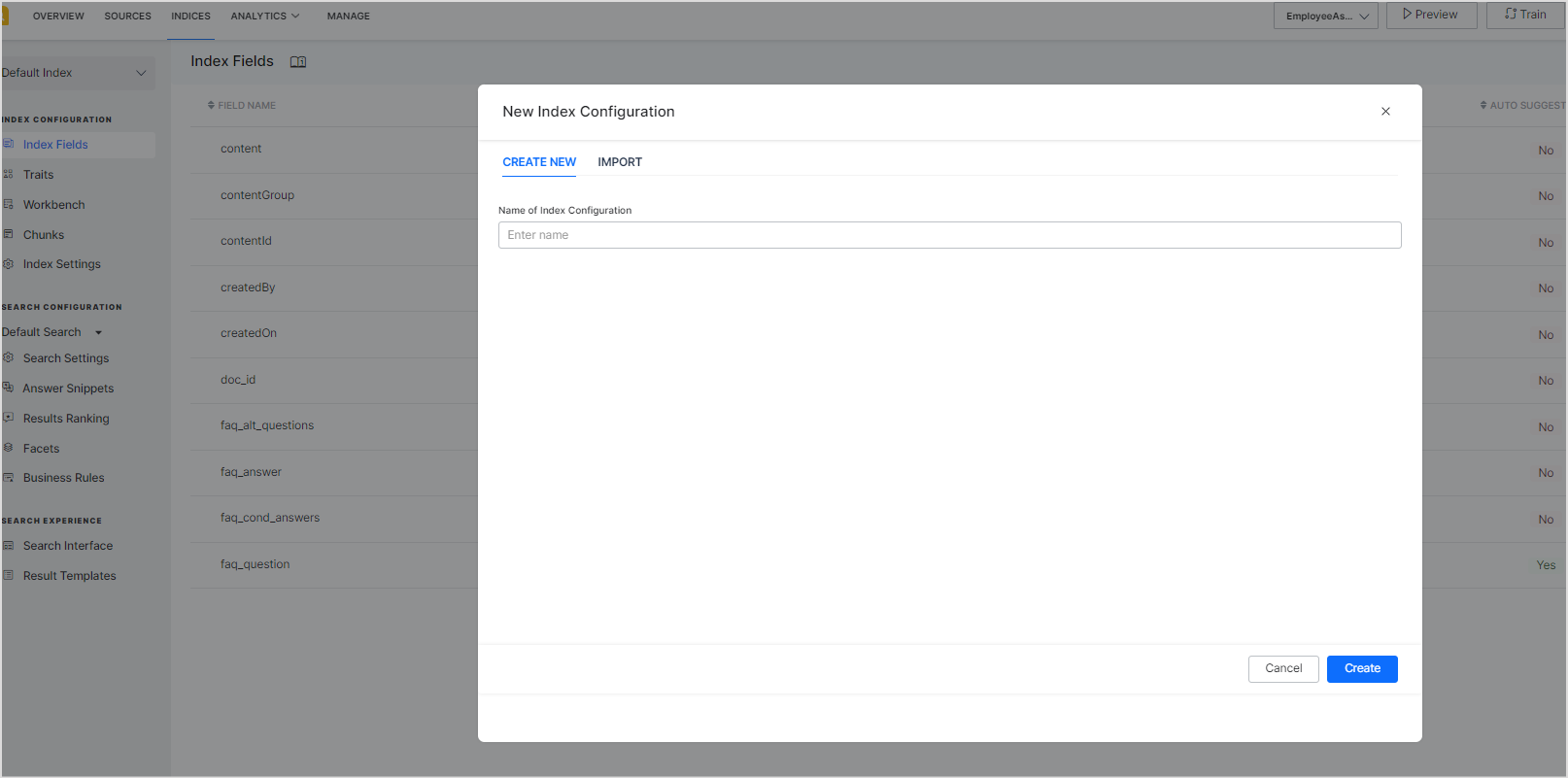
To create a new Index Configuration, click on the drop-down icon and select + Create New option.
Enter the name for the configuration and click Create.
Alternatively, you can also import an Index Configuration from a JSON file or clone an existing configuration.
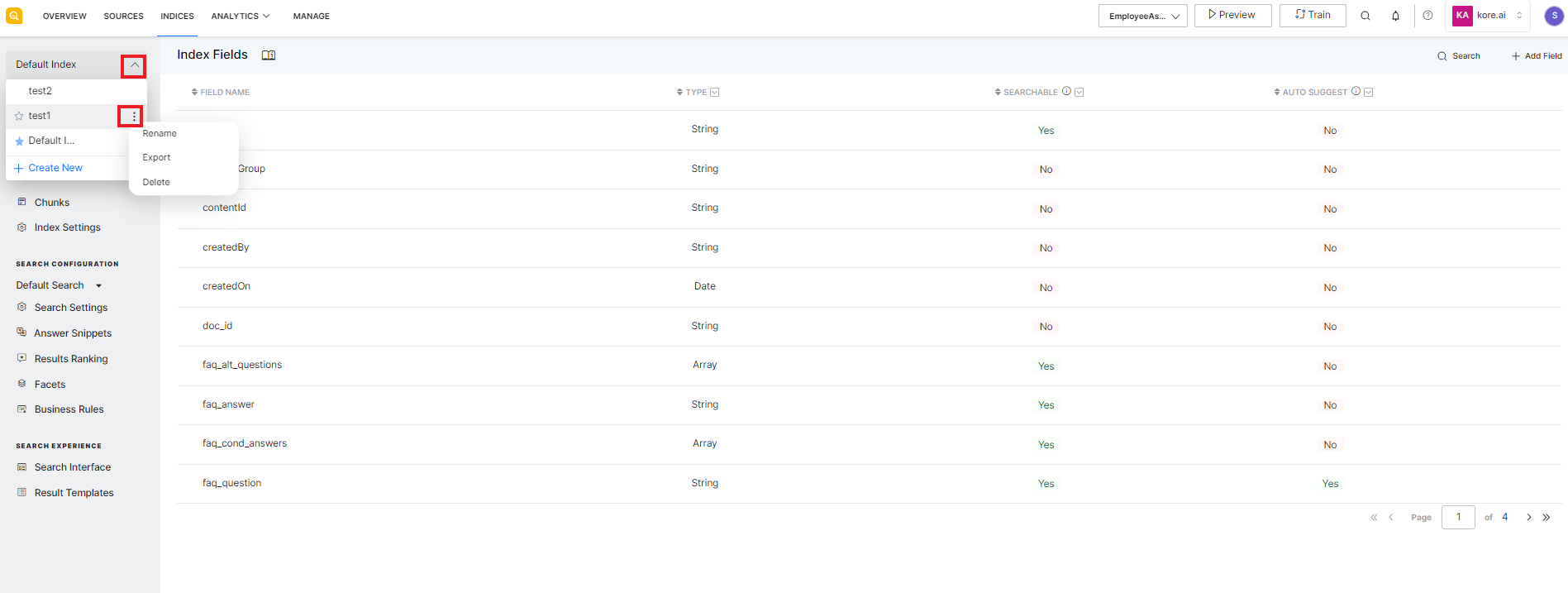
To rename, delete, or export an existing configuration, go to the list of configurations, click on the ellipsis icon, and take appropriate action.
You can create any number of index configurations to experiment and test before selecting the most appropriate configuration for your business needs. In the same manner, for each index configuration, you can create multiple search profiles to experiment with the various search options provided by SearchAssist.
When there are multiple Index Configurations, you can choose to set any of the configurations as the default one. A default configuration is the one used for preparing the results or answer index and for responding to the user queries. In other words, the parameters and settings under the default configurations are the ones in effect.
To make a given configuration as the default configuration for the application, click the star icon to the left of the name of the configuration.