Facets allow users to refine their search results by selecting appropriate filters based on the field values. These filters are used to fine-tune the search results and category listings without scrolling through innumerable pages. For example, in an eCommerce search, options to select the price range for the product or to filter the results based on the color of the product are provided.
SearchAssist application allows you to configure and manage facets. You can mark any indexed fields as a facet. Enabling the facet allows the search user to view the filters associated with the search results and also the count of matched results in the filter.
The SearchAssist application allows you to define two types of facets:
- Range Facet is used for filter attributes that have a defined range of values such as price, age, etc. It returns the result within the selected range. In product search scenarios, the Range facet is used to choose the price value of a product. For example, on an e-commerce website, you can use Range Facets to show all smartphones in the range of $1000 to $20000.
- Value Facet is used for filter attributes that are treated as labels such as colors, gender, etc.
You can configure both single-select and multi-select facets. The multi-select facet allows you to customize whether a user can select only a single item or multiple items in a filter. You can also customize the order in which the filters are displayed to the user by simply drag and drop operation.
Add Facets
To add facets, follow the below steps:
- Click the Indices tab on the top.
- On the left pane, under the Search Configuration section, click Facets.
- On the Facets page, click Add Facets.
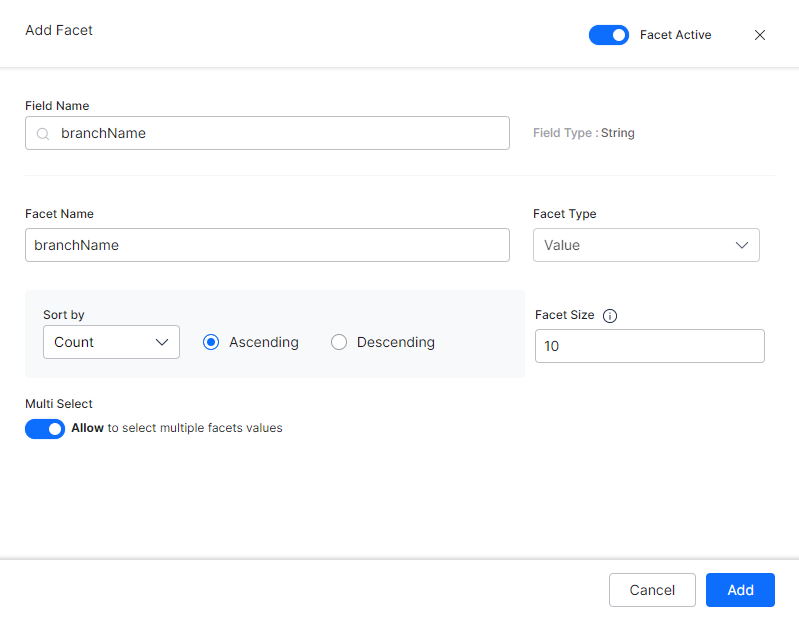
- On the Add Facet dialog box, in the Field Name field, search for a field and select it.
- Enter a name in the Facet Name field.
- Select the type from the Facet Type drop-down list as either Range or Value.
- For the Value type facet, you can further customize the user experience by configuring the following details:
- Facet Size is the number of Facet values provided to the user for selection.
- Facet values to be provided Sort by
- Ascending or Descending value of Count
- Ascending or Descending value of Label
- For the Range type facet, you can further customize the user experience by configuring the following details:
- Optional Range Name, if not provided, then the range is displayed as the name for the user.
- From and To values to be provided to the user for selection.
- You can add multiple ranges.
- You can turn on the Multi-Select toggle to allow the user to select multiple facets values.
- Click Add.
Action
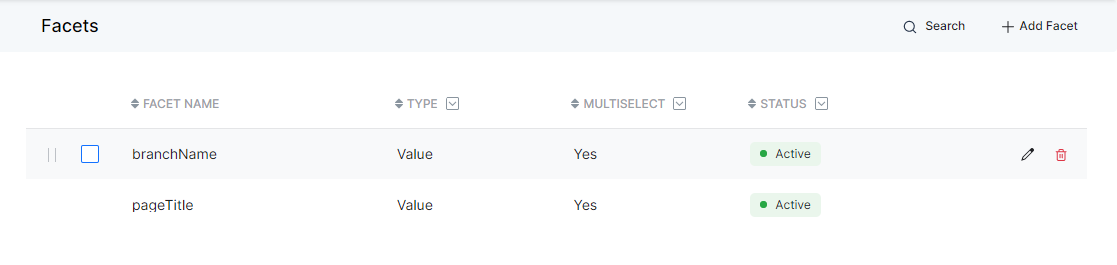
You can achieve the following from the Facets list view page:
- Search for a given Facet by name.
- Filter the Facets on Type, Selection criteria, and Status.
- Edit or Delete a Facet using the edit/delete icons. You can also delete facets in bulk with the Bulk Select option.
- Using the handlebar against each facet, you can specify the order in which facets are presented to the user.