SearchAssist supports a ‘meta_data’ field that allows you to add custom information to your document metadata or record. This is useful as it enables you to add filters or business rules based on this field. You can either manually add this field to the data, like in the case of structured data, or use a workbench stage to incorporate this field. Find more information on the meta_data field and how to use it here.
This document describes how to use Workbench to include the meta_data field in the extracted content.
Workbench tool provides you with different types of stages for different types of processing on the extracted content. To add a new field to the extracted content, we can use either the Field Mapping Stage or the Custom Script stage, depending upon the value to be .inserted to the field.
For illustration, let’s incorporate the following field into content crawled from web pages.
"meta_data": { "owner": "<value>" }
- Go to the Workbench and add the Custom Script stage. Refer to this guide to learn how to add a new stage.
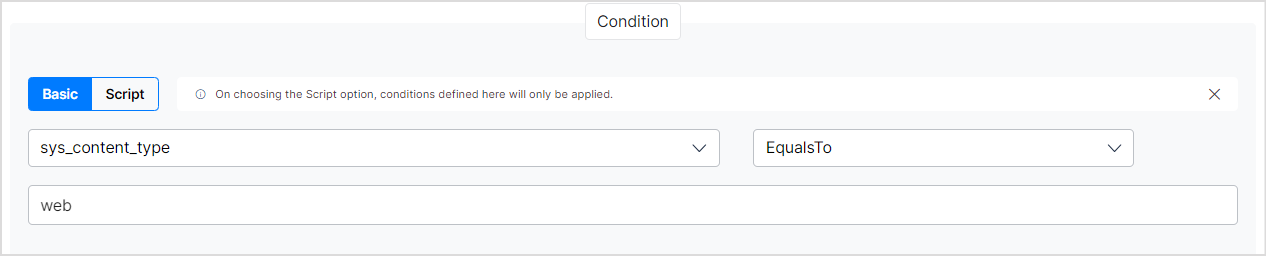
- Since we are processing the web page content, set the condition as follows:
- Next, add the script to create a new field meta_data with your custom JSON data. You can use the following script.
//Create your JSON in string format. ctx.str_owner="{\"owner\":\"John\"}"; //Add meta_data field to the document and set the JSON object as its value ctx.meta_data= Processors.json(ctx.str_owner); //Update the value of the custom field as required. ctx.meta_data.owner="Harry";
You can now this custom metadata for further processing of data in Workbench or filtering results.