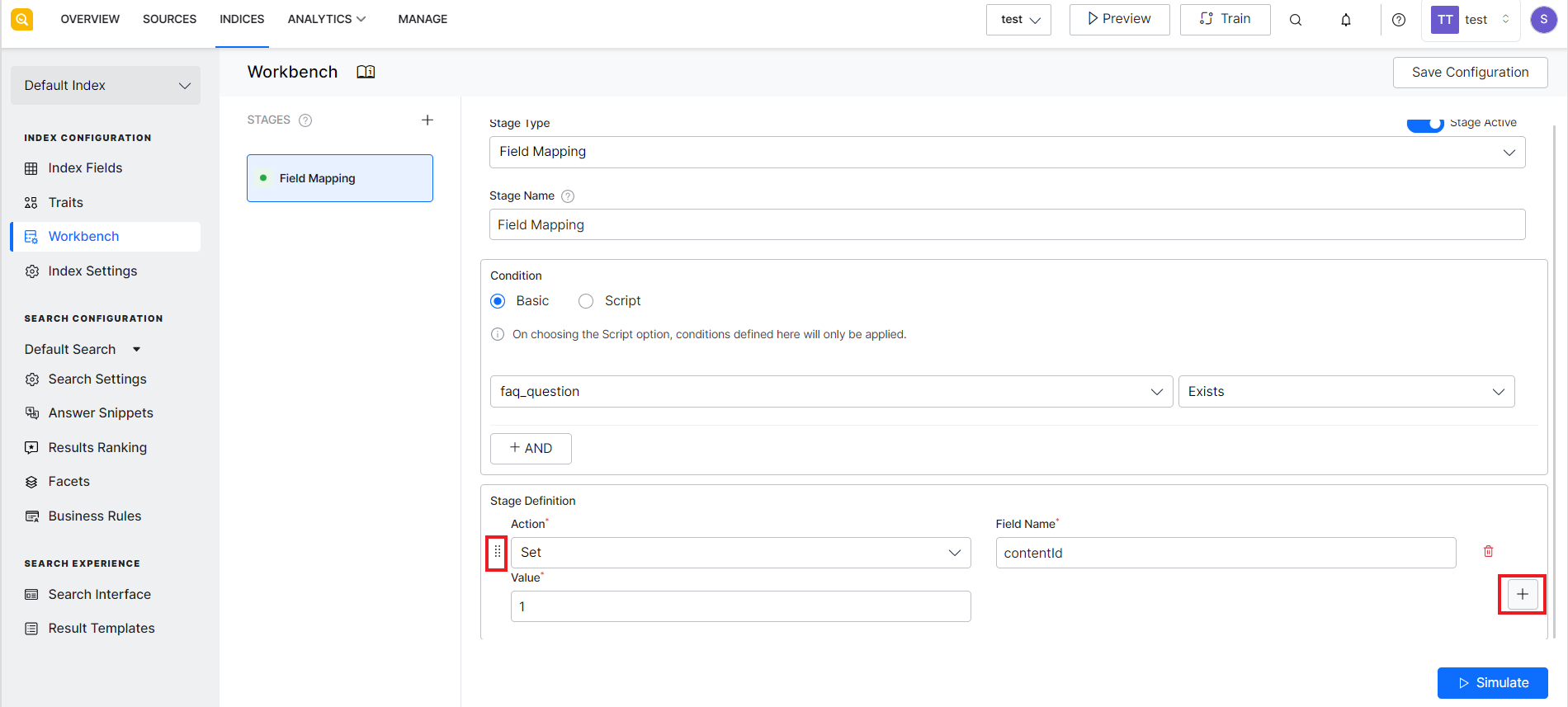
The Field Mapping stage can be used to map fields in a document to a target field. The mapping is performed on the fields that satisfy the conditions defined for the mapping. SearchAssist allows you to perform the following operations on the fields:
- Set the value of a field value
- Rename a field
- Copy the value of one field to another
- Remove a field
To define this type of stage, go to the workbench, add a new stage and set the stage type to Field Mapping. 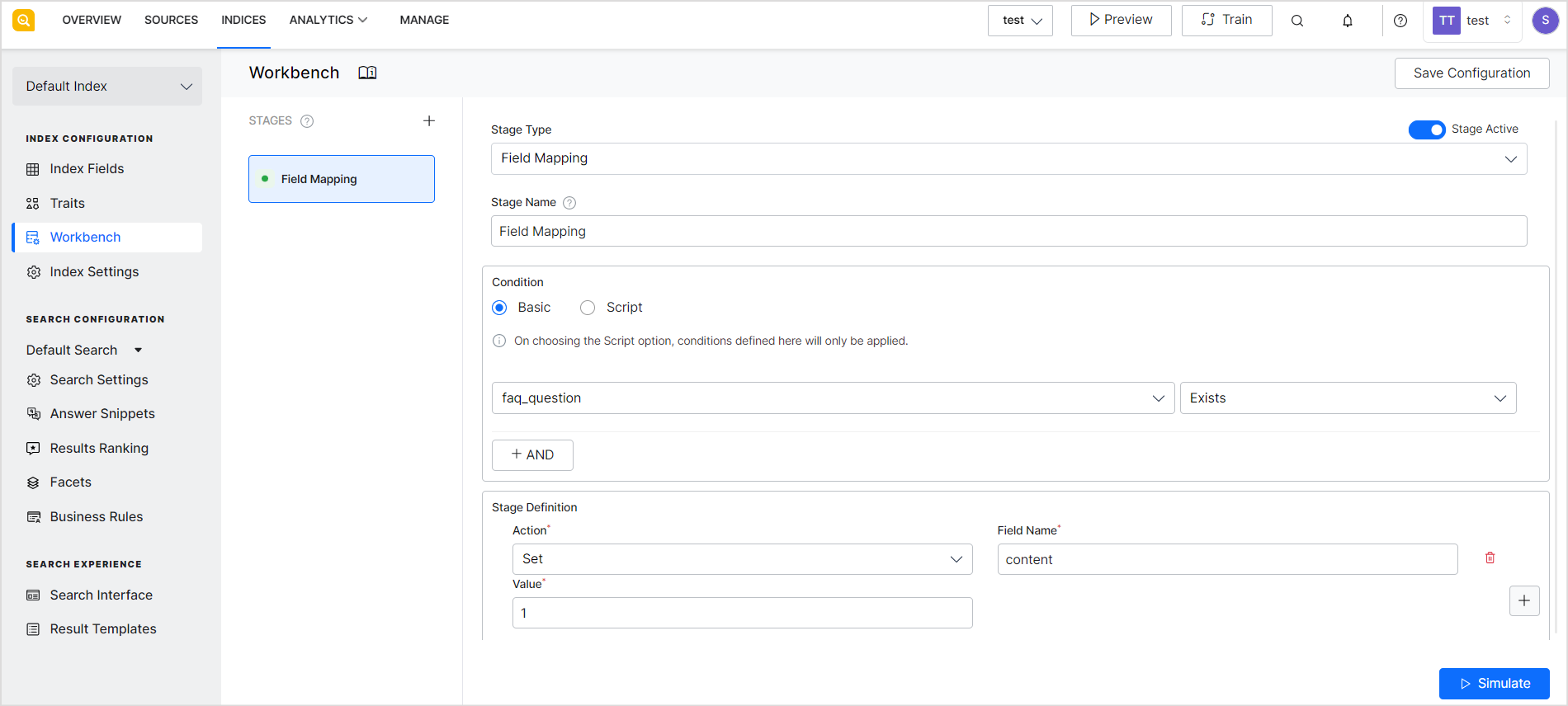
Field Mapping Configuration
The field mapping configuration has the following configuration properties:
- Stage Name – the name used to identify the index pipeline stage uniquely.
- Condition – Criteria to select the data on which field mapping is to be performed. There are two ways of defining the condition for the mapping: Basic and Script. When using the Basic method, you can define a condition using the index fields and operator. For example, if you want to perform field mapping for fields in file type of content, use the index field, ‘file_content’ and operator, ‘exists’ to define the condition to select the type of data on which processing is to be done. You can use the logical AND operator to add more than one check in a condition. When using the Script, you can provide a custom script to add your condition for field mapping.
- Stage Definition – Set of rules to define the changes to be made to the fields which satisfy the conditions. You can add more than one set of actions. When there are multiple actions defined, the actions are applied one after the other in the sequence in which they are defined. Use the + icon to add multiple actions to the stage definition and use the draggable dots icon to arrange the actions in the desired order.
You can take the following actions on the fields:
| Set | Sets the value of a particular field. It overrides the existing value of the field. |
| Rename | Renames the selected field |
| Copy | Copies the value of the source field to the target field. |
| Remove | Removes a particular field from the document. |