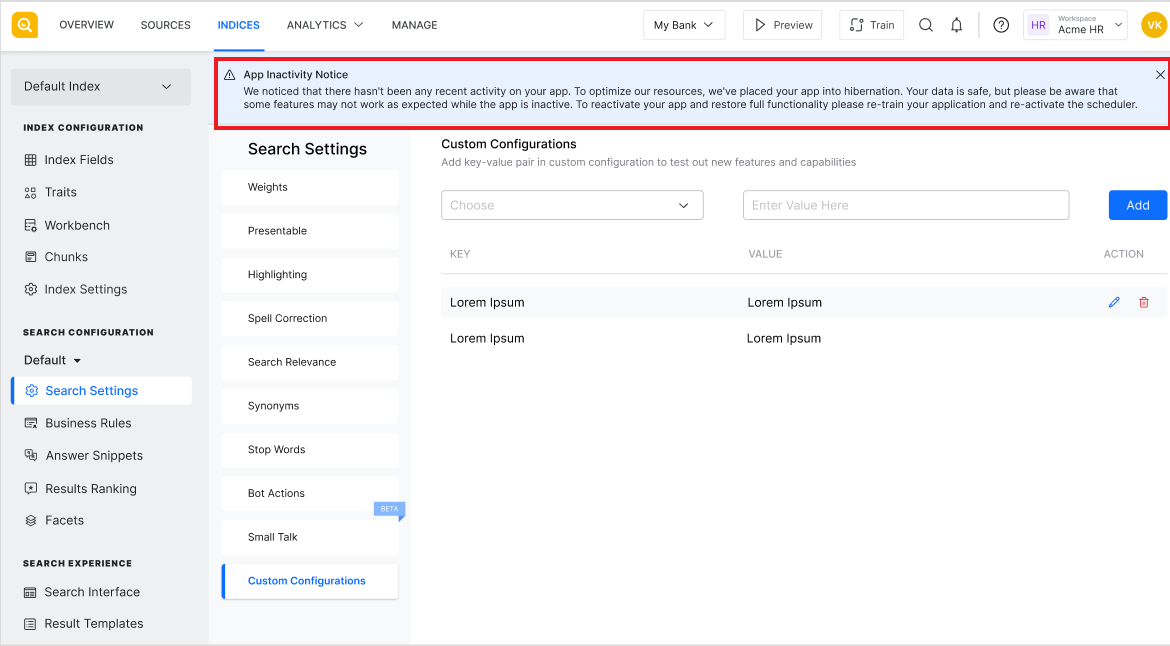
Smart Hibernation is a resource management feature that intelligently reduces resource consumption by putting inactive applications into hibernation. This helps optimize system performance, ensuring resources are not wasted on applications that are not in use while keeping them easily accessible when required.
The Smart Hibernation feature will be activated from November 16th, 2024.
How Does Smart Hibernation Work?
Applications enter hibernation if they meet the following two criteria:
- The app was created 90 or more days ago.
- If the last search query made by the end-user was more than 90 days ago
Once in hibernation, the app remains dormant until it is accessed again. A hibernated app is indicated through a banner on top of the application.
Benefits of Smart Hibernation
Smart Hibernation offers a way for optimum use of resources. It only applies to inactive applications. This ensures that resources are allocated efficiently to the active apps while inactive applications are not consuming unnecessary resources.
Activate a Hibernating App
To reactivate a hibernated app, access the application and retrain it. After retraining is complete (the time required depends on the amount of content ingested), the application is ready for use.
Key Points
- Data security: The application data remains fully intact and secure, even while the app is in hibernation.
- No impact on active apps: Applications accessed regularly continue to function as usual and have no impact.
- Instant reactivation: A hibernated app can be reactivated instantly by initiating the application training.
- Automatic application of the feature: Smart Hibernation is applied to all applications automatically, so no manual intervention is required.