Data forms an integral part of any search. It also plays an important role to understand customers’ needs and achieve customer satisfaction. Businesses obtain or import data from different sources and validate it, before presenting it to the customer or the end-user.
In SearchAssist, Adding Data allows you to fetch data from various sources and ingest it into the application. It helps you to evaluate the search users’ requirements and provide better services. For example, a bank that uses the SearchAssist application needs to cater to user queries related to products, services, and general inquiries. This data might exist in multiple locations, with different departments being the owners. To assist search users with their queries, business users need to fetch the data from these various sources and ingest it into the application thus serving a solution for those queries in one place.
Sources
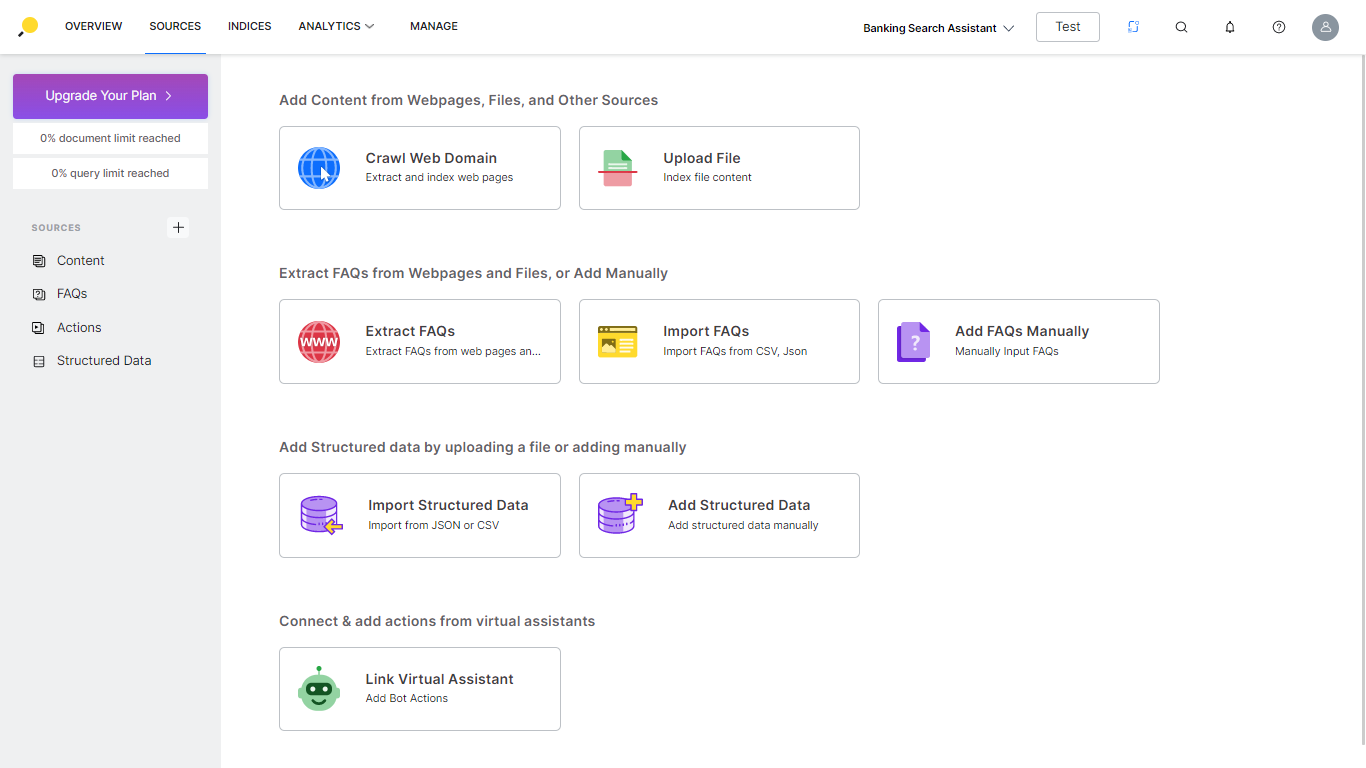
Sources refer to web pages or files from which the information needs to be obtained by the SearchAssist application. SearchAssist extracts data from varied sources like enterprise records to web pages and indexes the relevant items to make the content search-ready.
The Source page allows you to add and manage sources. You can add and manage sources through:
- Content – Content refers to the data obtained from external sources through web crawling or file uploads. The SearchAssist application parses this content and adds to the search index. For more information, refer to Content.
- FAQs – The Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) are a list of common questions that your customers ask about your products or services. For more information, refer to FAQs.
- Bot Actions – Bot Actions are a list of tasks that are performed by the linked virtual assistant. For more information, refer to Bot Actions.
- Structured Data – Structured data is an object, a set of key-value pairs from sources like databases, connectors. These can be extracted and formatted as JSON or CSV structure and ingested into SearchAssist. For more information, refer to Structured Data.